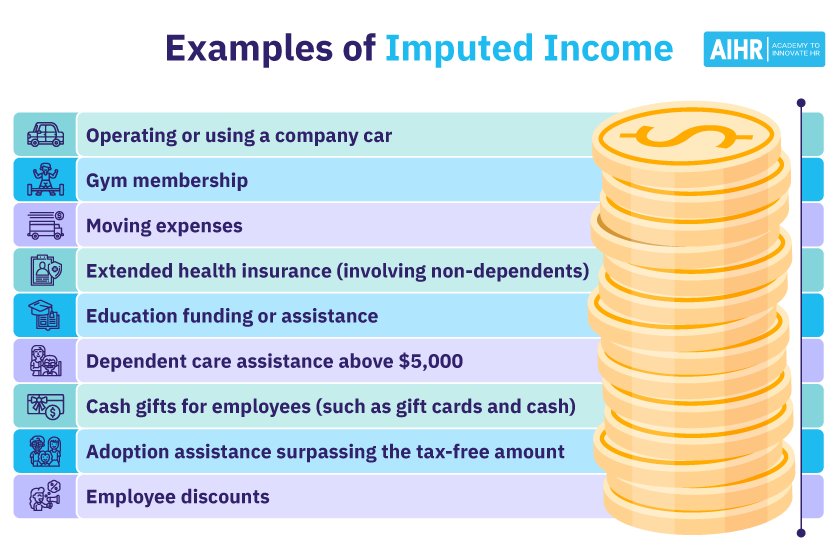
Imputed income can easily become a puzzling term for many. Simply put, imputed income refers to the value of non-monetary benefits provided by an employer to an employee. These benefits are considered as taxable income, even if no actual money exchanges hands. From company cars to housing allowances, imputed income impacts both employers and employees. Understanding how imputed income works is crucial for ensuring compliance with tax regulations and maximizing financial planning strategies. Let’s delve into the world of imputed income and unlock its significance in the realm of personal and corporate finance.
Understanding Imputed Income: What You Need to Know
Have you ever heard of the term ‘imputed income’? It may sound complicated, but don’t worry, we’re here to break it down for you in simple terms. In this article, we will explore the concept of imputed income, how it affects individuals, and why it is important to understand. So, sit back, relax, and let’s dive into the world of imputed income!
What is Imputed Income?
Imputed income is a term used to describe the value of non-monetary compensation or benefits that an individual receives from their employer. These benefits are not received in the form of cash but are considered as part of the individual’s total income for tax purposes.
For example, if an employee is provided with a company car for both business and personal use, the value of this benefit is considered imputed income. Similarly, if an employer offers housing or meals to an employee, the value of these benefits would also be considered imputed income.
Types of Imputed Income
There are several types of imputed income that individuals may encounter in their professional lives. Let’s take a closer look at some common forms of imputed income:
Health Insurance Benefits
One of the most common types of imputed income is health insurance benefits provided by an employer. When an employer covers the cost of health insurance for an employee, the value of these benefits is considered as imputed income. This is important to note because it affects the employee’s total income and may have tax implications.
Company Cars
Another common form of imputed income is the provision of a company car for both business and personal use. The value of using the company car is considered imputed income and must be reported for tax purposes. This is because the personal use of a company car is seen as a form of compensation.
Employee Discounts
Employers may also offer employee discounts on products or services as a benefit. The value of these discounts is considered imputed income and must be included in the employee’s total income for tax purposes. This is because the discounts are seen as a form of compensation provided by the employer.
Why Imputed Income Matters
Understanding imputed income is essential for both employers and employees. For employees, being aware of imputed income helps them accurately report their total income and comply with tax regulations. Failing to report imputed income can lead to penalties and legal issues.
For employers, understanding imputed income is crucial for accurately calculating employee compensation and benefits. By correctly identifying and valuing imputed income, employers can ensure compliance with tax laws and avoid potential audits or fines.
How Imputed Income is Calculated
Calculating imputed income can be a complex process, as it involves determining the fair market value of the non-monetary benefits provided to an employee. Employers may use various methods to calculate imputed income, including appraisals, industry standards, or IRS guidelines.
It is important for both employers and employees to keep detailed records of imputed income and the methods used to calculate it. This information may be requested during tax audits or reviews, so having accurate documentation is crucial.
Implications of Imputed Income
Imputed income can have several implications for both employees and employers. From a tax perspective, imputed income is subject to federal, state, and local taxes, just like regular income. This means that individuals receiving imputed income may have additional tax obligations to fulfill.
Additionally, imputed income can impact eligibility for certain government benefits or programs that are based on income levels. By accurately reporting imputed income, individuals can ensure that they are not disqualified from these benefits due to underreporting.
Imputed income is an important concept that affects both employees and employers. By understanding what constitutes imputed income, how it is calculated, and its implications, individuals can ensure compliance with tax regulations and avoid potential legal issues.
Remember, imputed income is just as significant as regular income and should be treated as such when it comes to reporting and tax obligations. So, the next time you receive non-monetary benefits from your employer, don’t forget to consider the impact of imputed income!
What is Imputed Income? Unlocking the Secrets and Maximize Your Earnings and Stay Tax Compliant
Frequently Asked Questions
What is imputed income?
Imputed income refers to the value assigned to non-cash benefits provided to an employee by their employer. This can include things like health insurance, company car usage, or housing provided by the employer.
How is imputed income calculated?
Imputed income is usually calculated based on the fair market value of the benefit provided. It can be determined using various methods, such as using the cost paid by the employer for the benefit, or through a formula set by the tax authorities.
Why is imputed income important?
Imputed income is important because it affects the tax obligations of employees. The value of imputed income is typically added to the employee’s overall income, which can impact the amount of taxes they owe.
Are all non-cash benefits considered imputed income?
Not all non-cash benefits provided by an employer are considered imputed income. Only specific benefits that have a cash value and are provided for the convenience of the employer are typically categorized as imputed income.
Final Thoughts
Imputed income plays a crucial role in tax calculations, especially for benefits provided by employers. It represents the value of non-monetary compensation that is taxable. Understanding imputed income is essential for individuals to accurately report their total income. By recognizing imputed income, taxpayers can avoid potential penalties for underreporting. In conclusion, being aware of imputed income helps individuals comply with tax regulations and maintain financial transparency.